Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is a powerful web analytics platform that provides businesses with tools to track and analyze user behavior on their websites. One of the key features of GA4 is conversion tracking, which allows businesses to track user actions that lead to a desired outcome, such as a sale or a lead generation form submission. In this article, we will delve deeper into GA4 conversion tracking and explore how businesses can leverage this feature to improve their website performance and achieve their marketing goals.
What is Conversion Tracking in GA4?
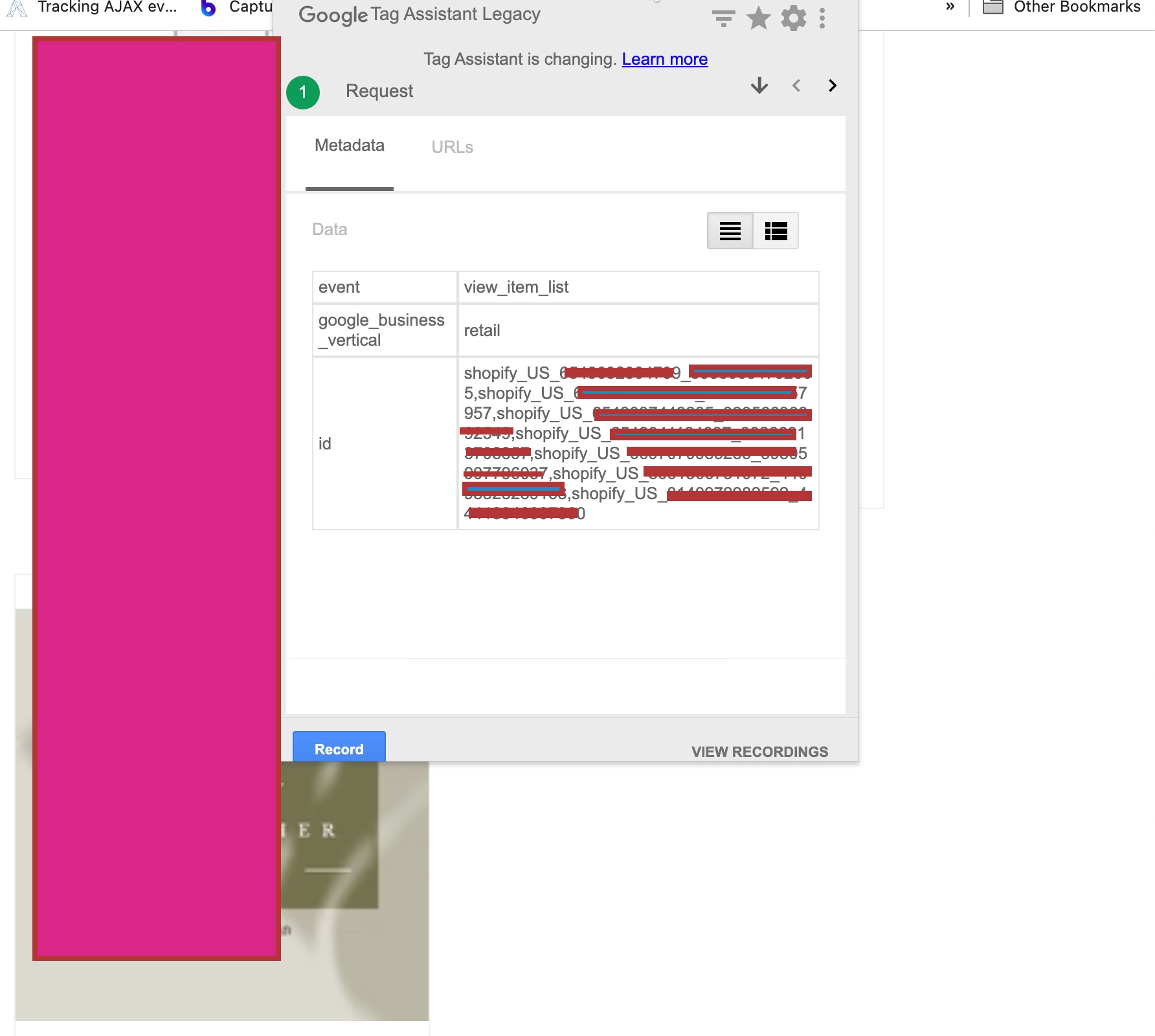
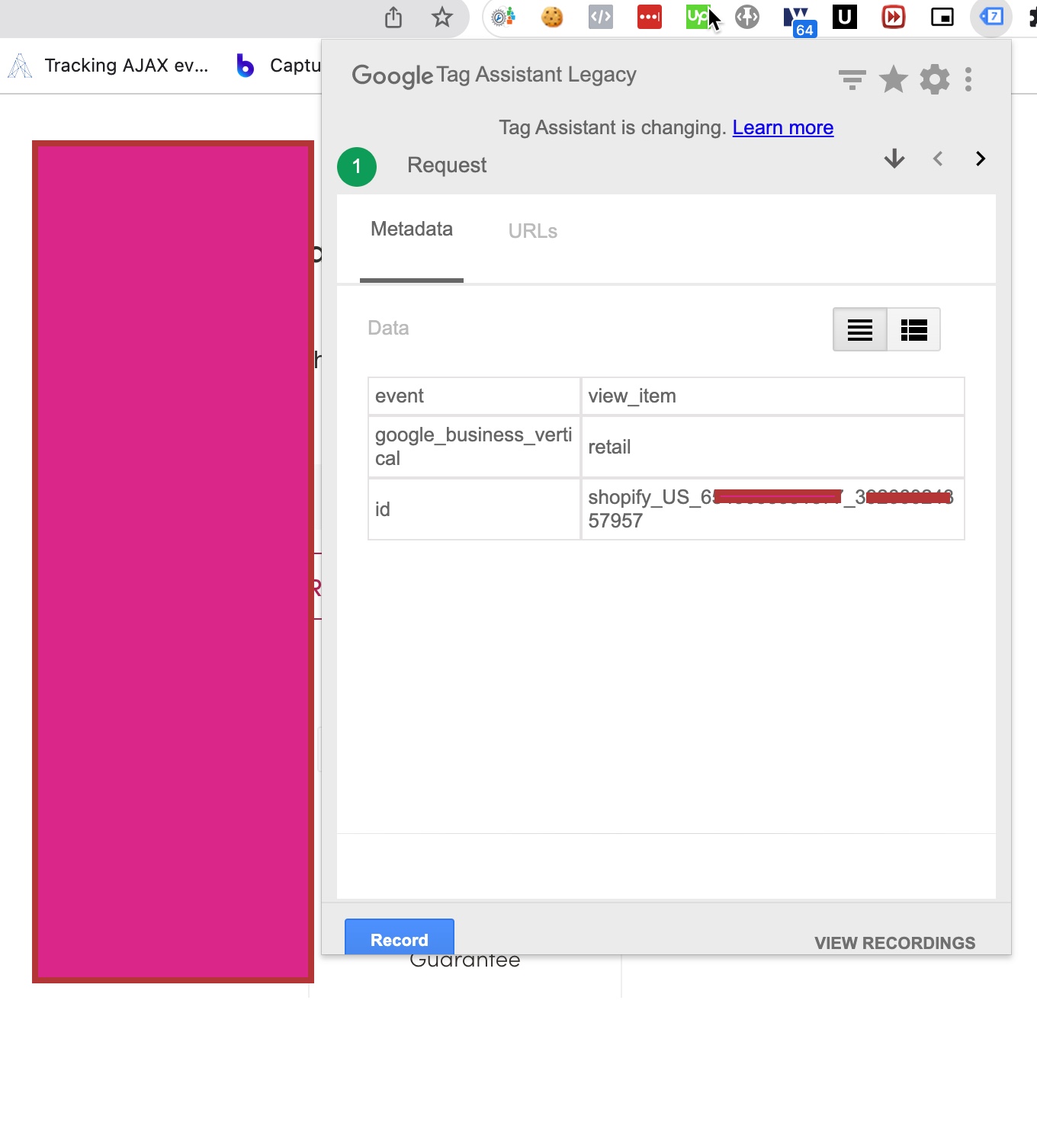
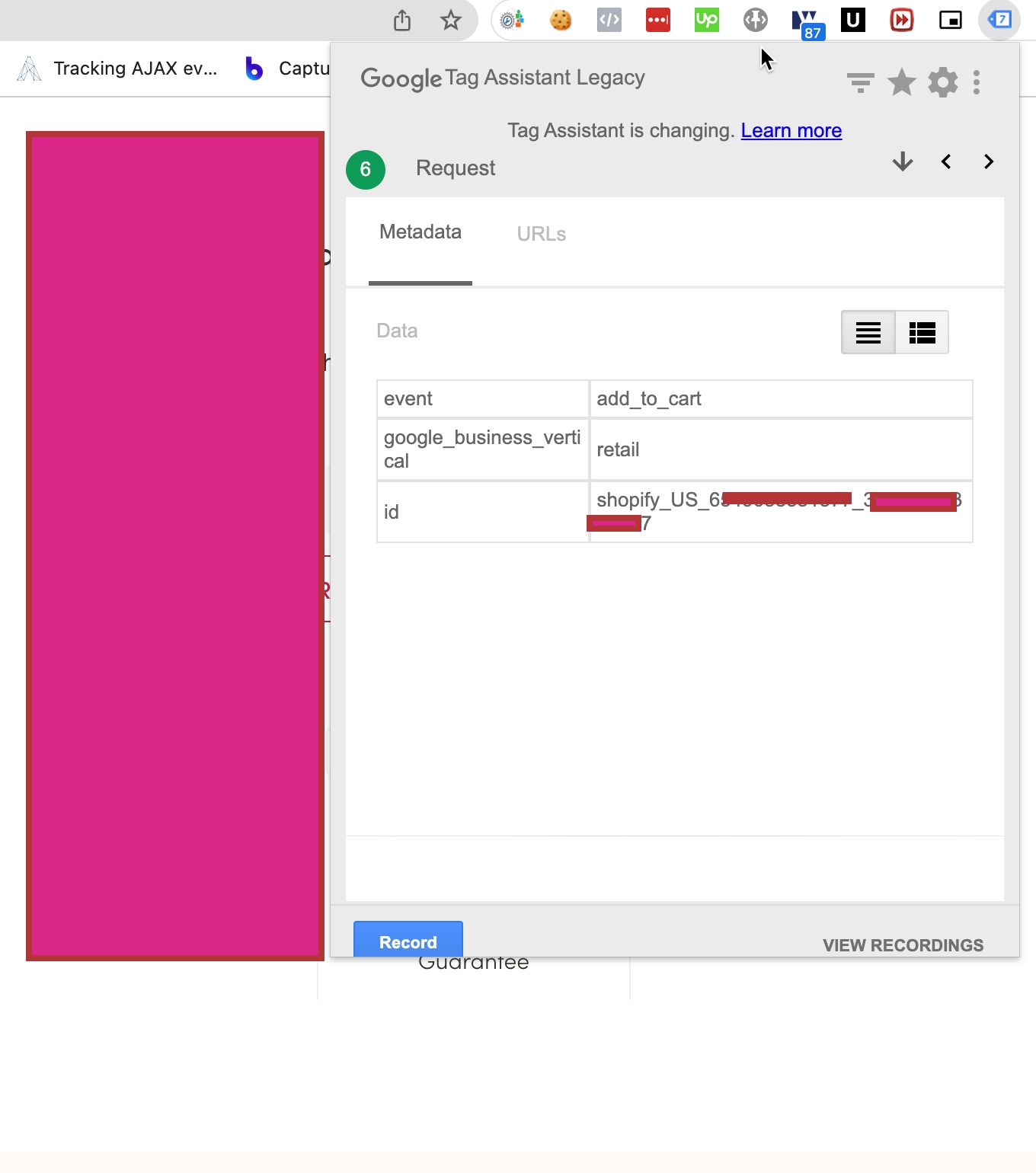
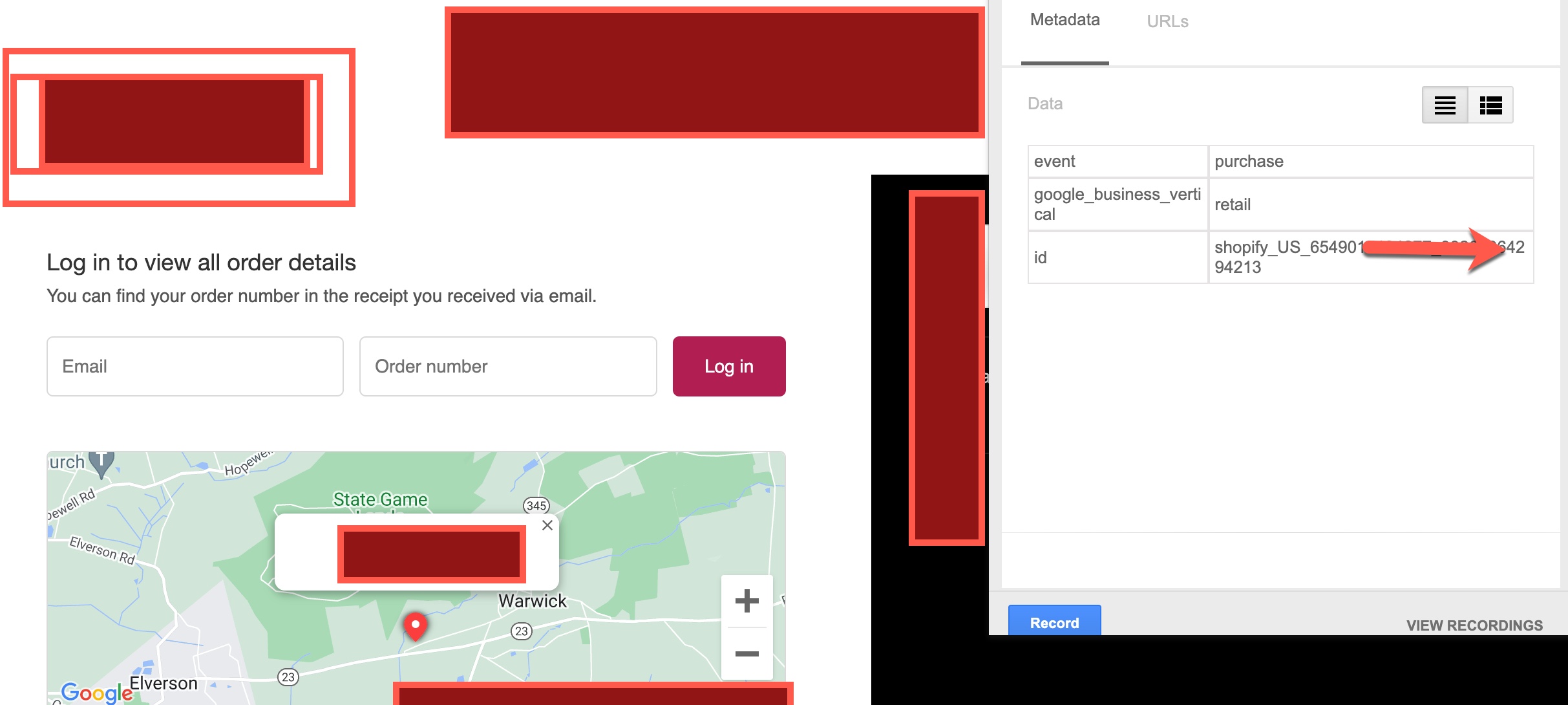
Conversion tracking is the process of tracking user actions on a website that lead to a predefined goal or outcome. In GA4, conversions are tracked through events. An event is an interaction that a user has with a website, such as clicking on a button or filling out a form. By tracking events, website owners can gain insight into user behavior and optimize their website to achieve their conversion goals.
Conversion tracking in GA4 can help businesses achieve a range of goals, including:
Increasing online sales: Conversion tracking can help businesses track the conversion rates of different products, product categories, and marketing campaigns to optimize their website and marketing strategies to increase sales.
Lead generation: Businesses can use conversion tracking to track form submissions, phone calls, and other actions that generate leads. By tracking these events, businesses can optimize their lead generation strategies and increase the number of high-quality leads they generate.
Improving user experience: Conversion tracking can help businesses identify areas of their website that are not performing well and make changes to improve the user experience, such as redesigning a checkout process or simplifying a lead generation form.
How to Set Up Conversion Tracking in GA4
Setting up conversion tracking in GA4 is a three-step process that involves defining conversion goals, creating conversion events, and setting up conversion tracking.
Step 1: Define Conversion Goals
Before setting up conversion tracking, businesses need to define their conversion goals. Conversion goals are the actions that users take on a website that are valuable to the business, such as purchasing a product or submitting a lead generation form. Businesses should identify the most important conversion goals for their website and set up conversion tracking for each of these goals.
Step 2: Create Conversion Events
Once businesses have identified their conversion goals, they need to create conversion events in GA4. Conversion events are the actions that users take on a website that trigger conversion tracking. Businesses can create conversion events for a wide range of actions, such as clicking on a button, visiting a certain page, or submitting a form.
To create a conversion event, businesses need to follow these steps:
- Log in to their GA4 account and click on the “Events” tab in the left-hand menu.
- Click on the “Create Event” button.
- Give the event a name and specify the event parameters, such as the category, action, and label.
- Choose the trigger for the event, such as a click or a page view.
- Set the conversion goal as the destination URL that users will reach after completing the event.
Businesses can create multiple conversion events for each conversion goal to track different actions that contribute to the overall goal.
Step 3: Set Up Conversion Tracking
The final step in setting up conversion tracking is to set up the tracking for each conversion event. To set up conversion tracking, businesses need to follow these steps:
- Click on the “Conversions” tab in the left-hand menu.
- Click on the “Create Conversion Event” button.
- Choose the conversion event that they want to track.
- Specify the conversion parameters, such as the conversion value and the currency.
- Choose the attribution model that they want to use to credit conversions to different marketing channels
Warning: If you don’t know about javascript or don’t have developing knowledge then don’t try to Google Analytics 4 Conversion Tracking Conversions that can break your site, Cart and other functionality
Disclaimer: Google tag manager belongs to Google property
For Contact: mappchero@gmail.com
I am available for Hire on Freelancer: Freelancer.com
I am available for Hire on Upwork: Upwork.com
I am available for Hire on Peopleperhour: Peopleperhour.com
I am available for Hire on Guru: Guru.com